Neurodiversity is a term that celebrates the vast range of ways human brains can function. While some people process information and interact with the world in a way considered “typical,” others experience these things differently. This is what it means to be neurodivergent.
If you’ve ever felt like your brain works in a unique way, you might be wondering, “How do you know if you’re neurodivergent?” There isn’t a single, definitive answer, but there are some common signs to look for. Many people seek out autism therapy services to better understand and support their neurodivergent experiences.

How Do You Know if You’re Neurodivergent?
The human brain is a marvel of complexity, and how it functions varies greatly from person to person. Neurodiversity celebrates this beautiful fact, recognizing that brains that operate outside the “typical” range can bring valuable strengths and perspectives. So, how do you know if you fall under the umbrella of neurodiversity?
There’s no single test to determine if you’re neurodivergent. However, some signs might indicate you experience the world differently. These can involve:
- Social Interactions: Does social engagement leave you feeling drained? Perhaps you struggle with making eye contact or interpreting nonverbal cues. These could be signs of neurodivergence.
- Sensory Processing: Do bright lights, loud noises, or certain textures feel overwhelming? This heightened sensitivity can be a sign of sensory processing differences, which are common among neurodivergent individuals.
- Focus and Attention: Does staying focused prove challenging, or do you find yourself hyperfocusing on specific interests? Difficulty regulating attention can be linked to conditions like ADHD, which falls under the neurodiversity umbrella.
- Learning Differences: Do you struggle with reading, writing, or math? These challenges can be indicators of dyslexia or other learning disabilities, which are also considered neurodivergent conditions.
It’s important to remember that everyone experiences these traits to some degree. The key factor is how significantly they impact your daily life. If you find yourself constantly struggling or feeling misunderstood, seeking a professional evaluation might be beneficial. This evaluation can help identify any underlying neurodevelopmental conditions.
The term “neurodivergent” encompasses a wide range of conditions. Some of the most common include:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): This spectrum includes challenges with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Individuals with ADHD may struggle with focus, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
- Learning Disabilities: These can manifest as difficulties with reading, writing, or math, such as dyslexia, dyscalculia, and dysgraphia.
- Down Syndrome: This genetic condition affects development and can cause intellectual and physical challenges.
Neurodivergence, after all, isn’t a deficit. It’s a different way of experiencing and interacting with the world. If you suspect you or someone you know might be neurodivergent, explore resources and support options. There’s a whole community out there celebrating neurodiversity and offering tools to thrive.

Signs That You’re Neurodivergent
While neurodivergence can manifest in many ways, some signs are more common than others. It’s important to remember that these signs exist on a spectrum. However, if you find these traits significantly impacting your daily life, it might be worth seeking a professional evaluation.
- Social Difficulties: People with neurodivergence may struggle to understand social cues like facial expressions, body language, or sarcasm. This can lead to misunderstandings and difficulty navigating social situations. They might crave social connection but find it challenging to build and maintain friendships.
- Sensory Processing Differences: The world can be an overwhelming place for some neurodivergent individuals. They might be hypersensitive to certain sights, sounds, smells, or textures. This can make everyday activities like going to the grocery store or attending a concert stressful or even unbearable.
- Focus and Attention Challenges: Difficulty focusing, hyperfocusing on specific interests, or fidgeting can be signs of conditions like ADHD. People with ADHD may struggle to stay on task, complete multi-step instructions, or manage their time effectively.
- Learning Differences: Dyslexia, dysgraphia, and dyscalculia are just a few examples of learning disabilities that can affect people with neurodivergence. These can manifest as challenges with reading, writing, math, or organization.
- Stimming Behaviors: Stimming, or self-stimulatory behaviors, are repetitive movements or actions used to self-regulate or cope with emotions. These can include rocking, tapping, hand flapping, or humming. While sometimes disruptive in social settings, stimming is a natural response for many neurodivergent people.
- Intense or Obsessive Interests: Having a strong fascination with a particular topic or object is another common sign. This passion can be a double-edged sword. While it can lead to deep knowledge and expertise, it might also make it difficult to focus on other areas of life.
- Following Routines: Many people enjoy routines, but for some with neurodivergence, they become essential for managing anxiety and feeling safe. Deviations from the expected schedule can cause significant distress.
- Difficulty Sleeping: Sleep problems are prevalent among neurodivergent individuals. Sensory sensitivities, trouble quieting the mind, or difficulty regulating emotions can all contribute to disrupted sleep patterns.
- Avoiding Eye Contact: While not a universal indicator, challenges with maintaining eye contact can be a sign of neurodivergence. It’s important to note that cultural norms also influence eye contact, so this sign should be considered alongside others.
- Heightened Anxiety: Anxiety is a common experience for many, but for those with neurodivergence, it can be particularly severe. Social anxiety, generalized anxiety, and phobias are all more common in this population.
Remember, this is not an exhaustive list, and every person experiences neurodivergence differently. If you suspect you or someone you know might be neurodivergent, a professional evaluation can provide clarity and open doors to support and resources.
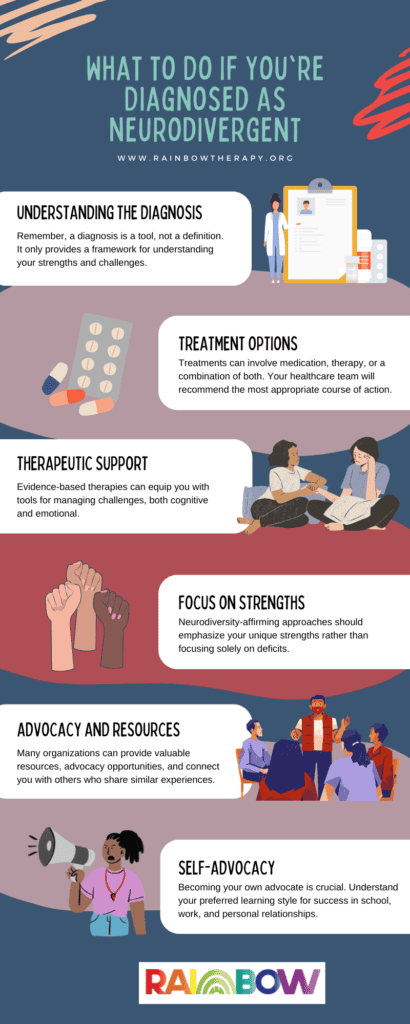
What to Do If You’re Diagnosed As Neurodivergent
A diagnosis of a neurodevelopmental condition can be both validating and confusing. While “neurodivergence” itself isn’t a diagnosis, it can be a helpful umbrella term for understanding your unique experiences. Here’s what to consider after receiving a diagnosis:
Understanding the Diagnosis
Remember, a diagnosis is a tool, not a definition. It provides a framework for understanding your strengths and challenges. There’s a spectrum within each neurodevelopmental condition, so your experience will be unique. Consulting with your healthcare provider to fully understand the implications of your diagnosis is crucial.
Treatment Options
There are no specific treatments for “neurodivergence.” However, there are highly effective treatments available for specific neurodevelopmental conditions like ADHD, dyslexia, or autism. These treatments can involve medication, therapy, or a combination of both. Your healthcare team will recommend the most appropriate course of action based on your individual needs.
Therapeutic Support
Even if you don’t require specific medical intervention, therapy can be immensely helpful. Evidence-based therapies can equip you with tools for managing challenges, both cognitive and emotional. Therapy can also improve your functional abilities in daily life, enhance your social awareness, and strengthen your interpersonal relationships.
Focus on Strengths
Neurodiversity-affirming approaches emphasize your unique strengths rather than focusing solely on deficits. This approach recognizes that neurodiverse individuals have diverse needs and talents. Therapists can help you identify and leverage your strengths, such as an exceptional ability to hyperfocus or heightened sensory perception.
Advocacy and Resources
Federal laws like the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) offer protections against discrimination. Seeking a diagnosis can be important for accessing these protections. Additionally, national organizations like the Neurodiversity Hub are dedicated to education and outreach on neurodiversity. These organizations can provide valuable resources, advocacy opportunities, and connect you with others who share similar experiences.
Self-Advocacy
Becoming your own advocate is crucial. Understanding and communicating your preferred learning and communication styles is essential for success in school, work, and personal relationships. Remember, many different learning styles exist, and advocating for your needs allows others to understand and support you.
Contact Rainbow ABA Today!
We understand that navigating neurodiversity can be challenging. Let Rainbow ABA be your partner on this journey. Contact us in Rainbow ABA today to schedule a free consultation! Our team of qualified professionals in New Jersey, Texas, and Georgia can help you assess your child’s needs and create a treatment plan to support their communication journey.
Sources:



